Bitcoin is the original and first cryptocurrency. Bitcoin, developed in 2009 by the enigmatic Satoshi Nakamoto, later introduced the world to modern cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology, and other concepts.
Learn everything there is to know about Bitcoin (BTC), its operation, and its underlying principles by taking a deeper look.
What is Bitcoin?
By definition, a cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, is a decentralised digital asset produced and stored online that enables peer-to-peer transactions without using conventional intermediaries like banks or governments.
With no centralised authority controlling its platform, Bitcoin is completely decentralised and run by its users. No one owns the technology that powers the internet or email, and the only people with any authority over Bitcoin are its users, investors, and developers worldwide.
History of Bitcoin
In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto originally suggested Bitcoin as a method to create a currency system. Independent of the world’s banks and financial organizations. but would function autonomously utilizing a blockchain, a distributed ledger system.
The value of bitcon in started off modestly; Historically, it passed the $1,000 threshold in January 2017 until topping that same year. Considering that it was the first cryptocurrency, its value has fluctuated greatly throughout the years, displaying tremendous volatility.
This did not deter investors, though, as its support base quickly expanded to include all people and companies that believe it has space to develop.
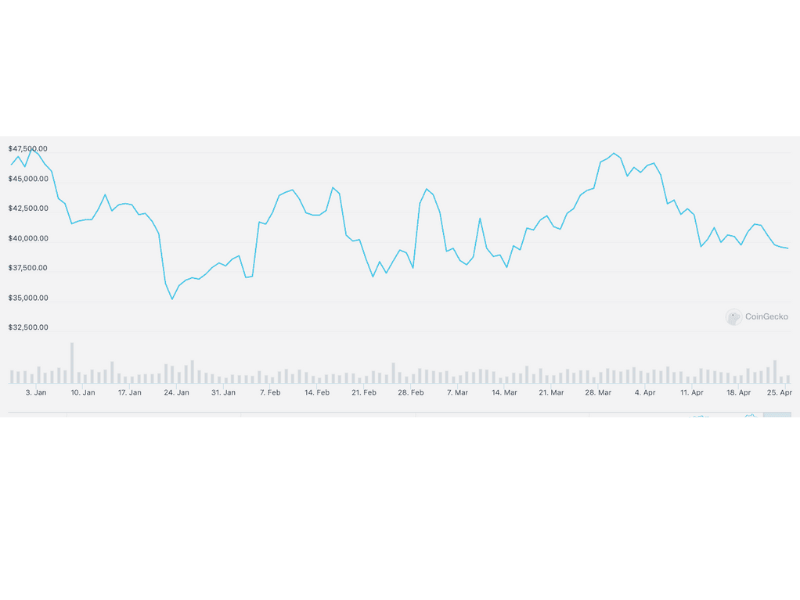
Price of Bitcoin (BTC) USD pairing in 2022.
Bitcoin (BTC) is one of the most traded cryptocurrencies, maintaining its status as the standard digital money for investors and holders.
It continues to be the biggest cryptocurrency with the highest market capitalization, and as of this writing, its worth is over $738 billion, ranking it in the top 15 most valuable traded assets in the world.
Fun fact: A famous Bitcoin transaction in the real world involved two Papa John’s pizzas. The price of the two bitcoin pizzas was 10,000 bitcoins (BTC), which today is equivalent to almost USD 300 million, making it the most expensive pizza transaction in recorded history (adjusted, of course, for inflation).
How is Bitcoin operated?
As stated in the introduction, Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer payment system that operates without a central controlling body, which normally regulates the supply of currencies.
Users directly manage the flow of Bitcoin by sending it from one wallet address to another. Additionally, the total supply is hard-capped at 21 million coins, turning it into a fixed asset with an expected long-term appreciation in value.
Understanding the many settings in which Bitcoin’s system operates is essential to understanding how it functions:
Blockchain
As was already established, Bitcoin is a digital currency that uses the blockchain, a decentralised ledger system.
Each transaction on this blockchain, which functions as a shared public ledger, is recorded as a block chained to the open-source coding. This technology is what made it possible for other cryptocurrencies to appear.
Private keys and Public keys
Your private and public keys are kept together in a cryptocurrency wallet where bitcoins are kept. Imagine these keys as the recipient and sender addresses for your Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Remember that accessing your assets requires both your private and public keys. These keys must be kept safe, period. Never give out your secret keys.
Bitcoin miners
Bitcoin miners are users of the site who independently confirm blocks of transactions using powerful computers. This process requires resolving an algorithm that verifies the legitimacy of transactions made on the blockchain. Then, miners receive Bitcoins as payment for their work.
How to store your Bitcoins: Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrencies profit from secure storage, just like you would if you kept your fiat money in wallets or banks.
A cryptocurrency wallet is where bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are kept. Different kinds of cryptocurrency wallets exist, with some having more functionality than others.
Bitcoin can be kept in a hardware cryptocurrency wallet called the Trezor One.
Understanding the two primary types of cryptocurrency wallets, hardware wallets (cold wallets) and software wallets (hot wallets), is essential when deciding which wallet is ideal.
Software Wallets
As the name suggests, cryptocurrency based on software wallets runs as programs or apps from your computer, tablet, or phone when they are online; this is why they are referred to as “hot wallets.”
The mobility, convenience, speed on-the-go trading of such wallets are their primary advantages. This makes them a popular choice for beginners.
The major danger and vulnerability associated with hot wallets is hacking and data leaks. Nevertheless, by utilizing strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and secure surfing strategies, you may still safeguard your hot wallets.
Hardware Wallets
Cold wallets, or hardware cryptocurrency wallets, are physical devices without an internet connection where you can save your Bitcoin and other digital assets.
The risk of potential hackers or bad malware creating issues your assets or credentials is effectively eliminated by these wallets – Which keep your information offline to authenticate and validate transactions.
The most secure ways to store your bitcoins and other digital currency holdings are generally thought to be hardware wallets. They need a little more knowledge and skill to set up effectively.
Superior hardware Trezor and Ledger are two crypto wallets with cutting-edge security features and industry-leading security measures to protect your digital valuables.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin
For those keen on investing, it pays to understand its pros and cons:
Pros
- Transparency: One of the core characteristics of Bitcoin is its innate transparency. Almost all the data relating to its supply and transaction history is publicly accessible on the blockchain, allowing anyone to verify it in real time.
- Security: Owners have total control over their transactions because the system is decentralised. Bitcoin payments can be conducted without giving any personal information related to the transaction.
- Freedom of peer-to-peer transactions: National borders, bank vacations, and administrative limitations have no impact on Coin. Anyone can send or get Btc at any time, across the world, as long as they have internet access.
Cons
Volatility:
- There is no disputing that Bitcoin is volatile by nature. This volatility is brought on by various variables, including but not limited to the fact that fewer companies are adopting bitcoins than there could be.Therefore, commercial activities, high trading volume, and other minor occurrences might greatly impact its price. However, as Bitcoin’s technology develops and its use is widely embraced by individuals and businesses worldwide, this volatility is anticipated to decline.
How to Buy Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is readily bought and sold in a secure environment through cryptocurrency exchanges. Another alternative for purchasing bitcoins is through specialised Bitcoin ATMs, – Where you may pay with cash or a debit card.
Reasons to Purchase Bitcoin
The idea of investing in Bitcoin could be worrying to some people. Although Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, in general, might be risky investments, they remain a well-liked alternative that aids in portfolio diversification.
The following are typical inquiries from persons looking to purchase this asset:
Is Bitcoin a wise financial decision?
If you can tolerate its volatility. It can an excellent is investment because of its high liquidity, transparency, and future. Furthermore, as previously indicated, Bitcoin’s supply is strictly limited to 21 million coins – Thus, as it approaches this number, its value is expected to rise steadily.
How can I buy Bitcoin Easily
Buying Bitcoin from trusted cryptocurrency exchanges is the most secure option. Typically, crypto exchanges offer higher rates, lower costs, and in our case, a coin switch option to make quick changes to your portfolio.








